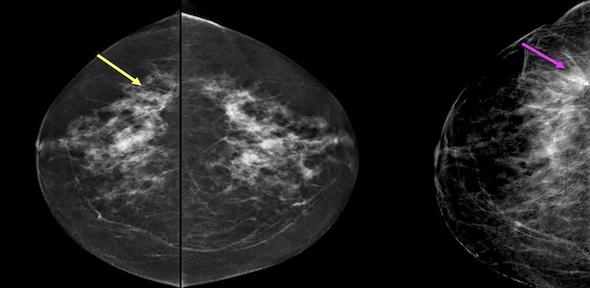
Breast screening enables early detection of cancers; however, most women have normal mammograms, resulting in repetitive and resource-intensive reading tasks. The aim of CMIH Hub researcher Yuan Huang and his colleagues was to investigate if deep learning (DL) algorithms can be used to triage mammograms by identifying normal results to reduce workload or flag cancers that may be overlooked.
In this retrospective study of 78,849 breast cancer screening mammograms, low-suspicion mammogram triage (99% sensitivity threshold) by DL algorithms indicated 35.0%–55.6% of mammograms to be reviewed by a lone reader, missing 0.0%–0.1% of screening-detected cancers. It was found that deep learning (DL) algorithms improved the efficiency and efficacy of breast cancer screening using a triage-based workflow. The study adds to the evidence base for using DL triage tools and tested realistic thresholds that can be applied to double- and single-reading programs. Furthermore, the research team demonstrated the performance of multiple commercially available algorithms within an independent research environment, addressing the gap in evidence highlighted in the UK National Screening Committee report 2021.
Read more about this work in Radiology.
Mammography Breast Cancer Screening Triage Using Deep Learning: A UK Retrospective Study
Sarah E. Hickman, Nicholas R. Payne, Richard T. Black, Yuan Huang, Andrew N. Priest, Sue Hudson, Bahman Kasmai, Arne Juette, Muzna Nanaa, Muhammad Iqbal Aniq, Anna Sienko, and Fiona J. Gilbert#
Radiology 2023 309:2

